DRI Technology
DRI Technology Overview
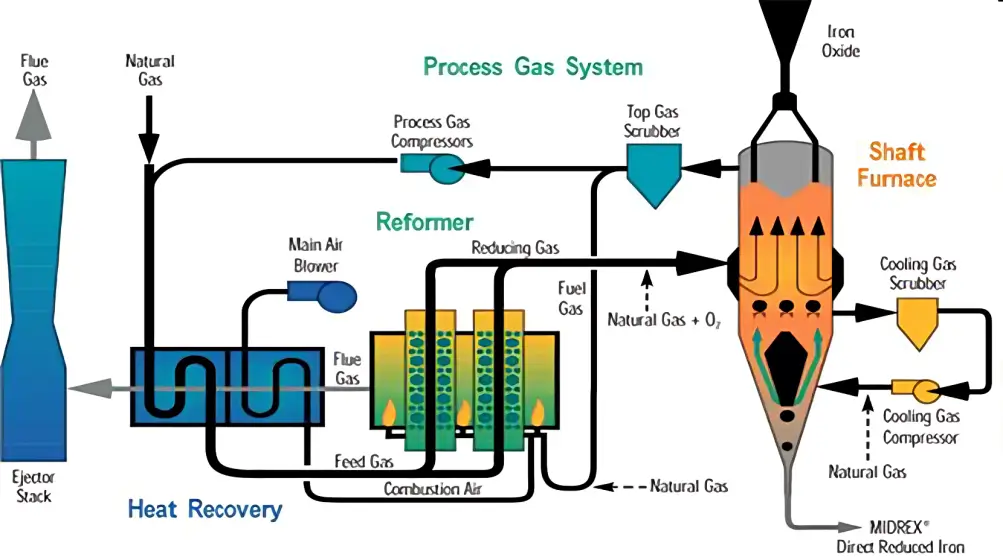
A MIDREX Direct Reduction Plant is composed of two main facilities: the Shaft Furnace, where iron ore is reduced, and the Reformer, which generates the reforming gas to be charged into the Shaft Furnace. The MIDREX® DRI` Process is able to use both lumps and pellets as the raw material and recycles the used gas.

Therefore, the process has both low energy consumption and low environmental impact, making it an environment-friendly process. The direct reduction of the oxide is carried out on a continuous basis. The iron oxide, fed to the top of the shaft furnace, flows downward under gravity and is discharged from the bottom in the form of direct reduced iron. The shaft furnace has two main gas circuits. In the upper circuit, iron oxide is preheated and reduced by counter flowing reducing gas, consisting of predominantly hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The lower circuit introduces a mixture of reducing gas and natural gas for the purpose of carburizing the direct reduced iron. The reducing gas is generated in the reformer by catalytically reforming a mixture of fresh natural gas and recycled top gas from the shaft furnace. The reformer is a refractory lined furnace containing alloy tubes filled with a nickel-based catalyst. The feed gas mixture flows upward through the catalyst bed where it is heated and reformed. The reducing gas leaves the reformer at near equilibrium conditions, containing 90 to 92 per cent hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The gas is then directly conveyed to the shaft furnace. The thermal efficiency of the reformer is greatly enhanced by the heat recuperator. This unit consists of two shell and tube type heat exchangers in the flue gas duct coming from the reformer. The heat exchangers recover the sensible heat from the reformer flue gas to preheat combustion air (used in the reformer burners) to 640 °C and to preheat the process gas (mixture of top gas and natural gas fed to the reformer tubes) to 540 °C.
DRI AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE IN THE STEEL SECTOR OF PAKISTAN
DRI is a virgin raw material produced by the reduction of iron oxide in the form of pellets or ore. In DRI process, iron ore is reduced in its solid state – unlike Blast Furnace process where a liquid metal is formed during reduction.
The initial investment of DRI / EAF (Electric Arc Furnace) plants are low compared to Blast Furnace steel plants. Though it has about the same iron content as pig iron (Blast Furnace Route), typically 92% – 94% average metallization.
There are two routes for DRI Production i.e. Gas based and Coal based. However, coal-based route involving rotary kiln process (primarily in India) has comparatively low metallization. Gas based DRI is the best quality DRI for high quality steel making.
Having consistent metallurgical properties and low percentage of gangue elements, it is the preferred input material for high precision CLEAN STEEL making. Due to this factor, it facilitates the operators of EAF to produce better grades of steel.
- • Currently, Gas based DRI is the most environment friendly technology versus the existing conventional steel making through the Blast Furnaces.
- • The ratio of carbon emissions of the Blast Furnace route of steel making versus DRI / EAF route of steel making is: 2.5 : 1
- • These days, for being environment friendly, DRI internationally is termed, “NAME OF THE GAME” in steel sector. Rapidly replacing Blast Furnaces with EAFs backed by the DRI Plants.